Dissecting a Multi-Stage macOS Infostealer
Summary#
I recently obtained a sample of a macOS infostealer that caught my attention for its operational sophistication. What initially appeared to be a straightforward Swift downloader revealed itself to be a well-engineered three-stage attack chain with some interesting anti-analysis and evasion techniques.
Concurrent analysis by Jamf Threat Labs has confirmed this sample is a variant of MacSync Stealer, a macOS infostealer operating under the Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model. The threat actor operates under the alias “mentalpositive” on underground forums. Apple has since revoked the developer certificate (Team ID GNJLS3UYZ4).
The sample, which I’m calling UserSyncWorker based on its internal naming, operates through a carefully orchestrated infection chain. The first stage is a Swift-based Mach-O binary that functions as a downloader, pulling a Zsh wrapper script from its primary C2 at gatemaden[.]space. That wrapper contains a Base64 and Gzip encoded payload which, when decoded, communicates with a secondary C2 at focusgroovy[.]com to retrieve AppleScript commands and exfiltrate harvested data.
What makes this sample notable is its defense evasion. The downloader programmatically strips the com.apple.quarantine extended attribute before executing downloaded payloads, bypassing Gatekeeper. Rate limiting logic prevents rapid re-execution, likely to frustrate sandbox analysis. Code signature validation ensures only payloads signed with a specific TeamIdentifier execute. These are not commodity malware techniques.
The final stage retrieves AppleScript dynamically via HTTP and pipes it directly to osascript for execution. Collected data ends up archived at /tmp/osalogging.zip before exfiltration. That “osalogging” naming convention is a strong indicator of keystroke logging or credential harvesting functionality.
Let us walk through the analysis.
Sample Information#
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Filename | malware (original name unknown) |
| File Type | Mach-O 64-bit x86-64 executable |
| Architecture | x86-64 |
| Framework/Platform | macOS / Swift |
| File Size | 285,488 bytes |
| SHA256 | 06c74829d8eee3c47e17d01c41361d314f12277d899cc9dfa789fe767c03693e |
| MD5 | aa3804744ef482e6c509a77511f98667 |
| Entry Point | 0x100003fb0 |
| Compilation Timestamp | Not recovered (Swift binary) |
| Campaign/Family | OSX.MacSync.B (MacSync Stealer) |
Attack Chain Overview#
Before diving into the technical details, here is how the full infection chain operates:
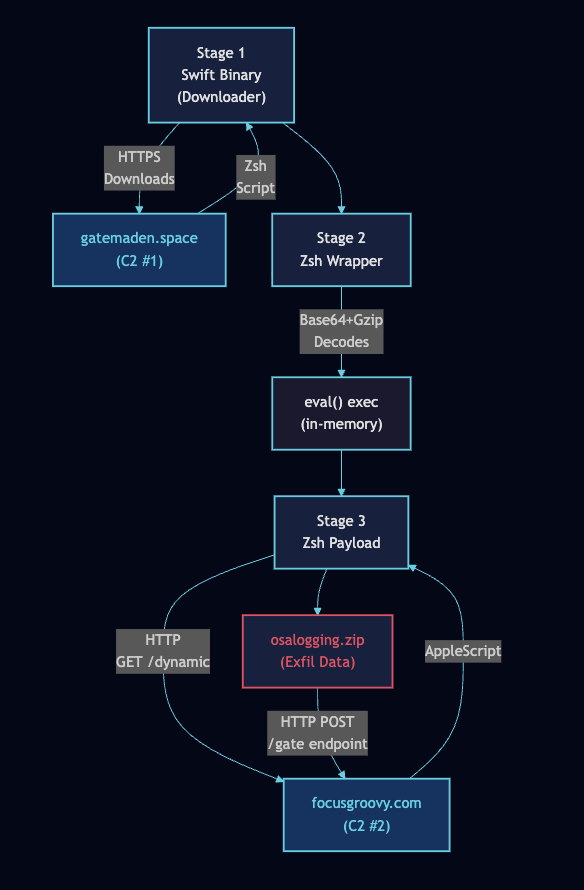
The stages unfold as follows:
Stage 1 initialises: Creates
~/Library/Application Support/UserSyncWorker/for state persistence and~/Library/Logs/UserSyncWorker.logfor activity logging.Connectivity check: Issues an HTTP request to
www.apple.comusing a dispatch semaphore for synchronous execution. Classic “am I online” check.Rate limiting: Reads
~/last_updateto determine if sufficient time has elapsed since previous execution. This prevents rapid re-execution and likely evades automated sandbox analysis that only observes short execution windows.Payload download: Downloads Stage 2 from
gatemaden[.]spaceusing curl with enforced TLS 1.2 minimum. ETag headers are cached to~/gate/etagfor conditional GET requests, reducing network noise.Signature validation: Validates the payload’s code signature using
codesignandspctl. Only payloads signed with TeamIdentifierGNJLS3UYZ4proceed. This is interesting operational security.Gatekeeper bypass: Removes the
com.apple.quarantineextended attribute from the payload, bypassing Gatekeeper enforcement.Stage 2 execution: The Zsh script is executed via NSTask. It decodes an embedded Base64+Gzip payload into memory and executes it via
eval, leaving no disk artifacts.Stage 3 daemonises: Redirects file descriptors to
/dev/null, then contactsfocusgroovy[.]com/dynamicto retrieve AppleScript commands.AppleScript execution: Retrieved AppleScript is piped directly to
osascriptfor execution without touching disk.Exfiltration: Uploads
/tmp/osalogging.ziptofocusgroovy[.]com/gatevia HTTP POST multipart form, then deletes the archive.
The Gatekeeper Bypass#
The most interesting technique in this sample is the programmatic Gatekeeper bypass. Here is what happens:
macOS applies the com.apple.quarantine extended attribute to files downloaded from the internet. This is the “quarantine flag” that triggers Gatekeeper to verify code signatures and potentially block unsigned or maliciously signed executables. Users see the familiar “This application was downloaded from the Internet” dialog.
UserSyncWorker bypasses this entirely. The downloader invokes xattr (or equivalent API) to strip the quarantine attribute before executing the downloaded payload:

It then calls spctl --assess --type execute to verify the bypass succeeded—this command returns exit code 0 for allowed applications and non-zero for rejected ones. This technique allows execution of payloads that would otherwise trigger Gatekeeper warnings or blocks.
The catch: this bypass requires the downloader itself to already be running with appropriate permissions. The initial infection vector likely involved user interaction or exploitation of a trusted application context. The downloader cannot bypass Gatekeeper for itself, only for subsequently downloaded payloads.
Code Signature Validation#
The downloader validates downloaded payloads using codesign -dv --verbose=4 and extracts the TeamIdentifier from the output. Execution proceeds only if the TeamIdentifier matches GNJLS3UYZ4.
| |
Note: The 2>&1 redirect is required because codesign outputs signature details to stderr, not stdout.
This serves dual purposes:
Operational security: Prevents execution of tampered or substituted payloads. If a researcher swaps out the payload, it will not run.
Attribution indicator: The operators possess a valid Apple Developer certificate, either legitimately obtained, stolen, or purchased. This is not commodity malware behaviour.
As noted in the Threat Intelligence section, Apple has since revoked this certificate.
Payload Obfuscation#
Stage 2 employs multiple obfuscation layers that make static analysis painful:
The outer Zsh script uses a randomised variable name (observed: d23670) and randomised heredoc delimiter (observed: PAYLOAD_m309032653423565). The inner payload is compressed with Gzip and encoded with Base64.
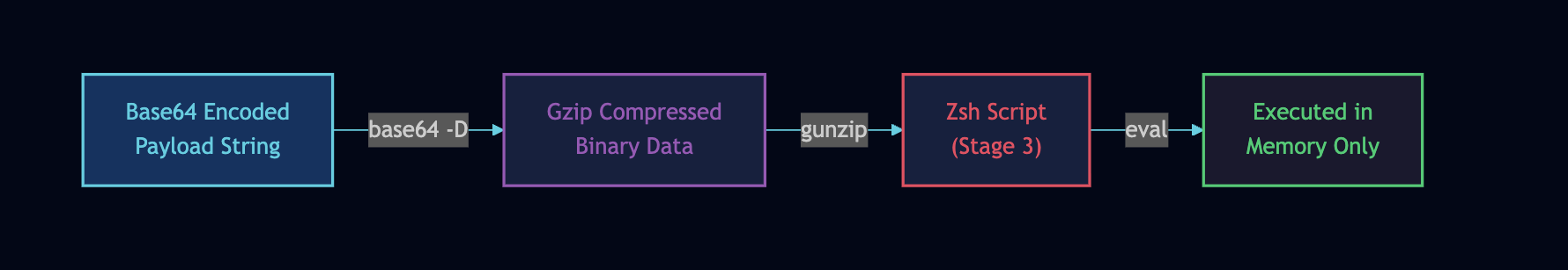
The eval execution model prevents the decoded script from touching disk. Only memory forensics or network capture would reveal the final payload in a live infection. This is exactly the kind of in-memory execution that makes incident response more challenging.
C2 Communication Protocol#
The C2 infrastructure uses two separate domains with different protocols:
Stage 1 to gatemaden[.]space (HTTPS):
- TLS 1.2 minimum enforced via
--proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 --tls-max 1.3 - Custom User-Agent:
UserSyncWorker/1.0 (macOS) - ETag caching for conditional requests
Stage 3 to focusgroovy[.]com (HTTP):
- Unencrypted HTTP (interesting choice)
- Chrome User-Agent masquerading:
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36... - API key header for authentication:
api-key: 5190ef1733183a0dc63fb623357f56d6
The shift from HTTPS to HTTP between stages is notable. It may indicate infrastructure limitations, different operators for each stage, or intentional design. HTTP reduces TLS inspection visibility on the exfiltration channel, though at the cost of enabling network monitoring to observe the traffic content.
Data Collection and Exfiltration#
The final stage uploads /tmp/osalogging.zip to the C2 server. The “osalogging” name strongly suggests the dynamically retrieved AppleScript performs one or more of:
- Keystroke logging via macOS accessibility APIs
- Screen capture
- Credential harvesting from Keychain
The exfiltration request includes the campaign token as the buildtxd form field, enabling the operators to correlate uploads with specific victims or campaigns:
| |
After successful upload, the script deletes osalogging.zip to cover its tracks.
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping#
| Technique | ID | Context in This Sample |
|---|---|---|
| Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript | T1059.002 | Stage 3 pipes C2 response to osascript |
| Command and Scripting Interpreter: Unix Shell | T1059.004 | Stage 2 Zsh wrapper; Stage 3 Zsh execution |
| Native API | T1106 | NSTask for process spawning |
| Subvert Trust Controls: Gatekeeper Bypass | T1553.001 | Removal of com.apple.quarantine attribute |
| Obfuscated Files or Information | T1027 | Base64+Gzip payload encoding |
| Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information | T1140 | Runtime decoding via base64 -D and gunzip |
| Masquerading: Match Legitimate Name or Location | T1036.005 | Chrome User-Agent in Stage 3 requests |
| Indicator Removal: File Deletion | T1070.004 | Deletion of osalogging.zip after exfiltration |
| Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion: Time Based Evasion | T1497.003 | Rate limiting between executions |
| Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | T1071.001 | HTTP/HTTPS C2 communication |
| Ingress Tool Transfer | T1105 | Payload download from gatemaden.space |
| Archive Collected Data | T1560 | osalogging.zip creation |
| Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | T1041 | HTTP POST to /gate endpoint |
Threat Intelligence and Attribution#
Open source intelligence research has positively identified this sample as a variant of MacSync Stealer, a macOS infostealer operating under the Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model. Jamf Threat Labs published concurrent analysis on 22 December 2025 confirming multiple exact indicator matches.
Attribution Confidence#
| Indicator | Match Status |
|---|---|
| Developer Team ID (GNJLS3UYZ4) | Exact match |
| C2 Domains (gatemaden[.]space, focusgroovy[.]com) | Exact match |
| Payload Path (/tmp/runner) | Exact match |
| Binary SHA256 | Listed in Jamf IOCs |
| Obfuscation (base64 -D | gunzip | eval) | Exact match |
| Function Name (daemon_function) | Exact match |
MacSync Stealer Evolution#
MacSync first emerged in April 2025 as “Mac.c Stealer” before rebranding. The variant analysed here represents the third generation of distribution methodology:
| Generation | Method | User Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Gen 1 (April 2025) | Drag-to-Terminal DMG | High |
| Gen 2 (Mid 2025) | ClickFix fake CAPTCHA | Medium |
| Gen 3 (December 2025) | Signed Swift dropper | Low |
This sample demonstrates a clear trend toward reducing user interaction requirements while increasing perceived legitimacy through code signing and notarization.
Certificate Status#
Apple has revoked the certificate associated with Developer Team ID GNJLS3UYZ4 following Jamf’s disclosure. Systems with updated XProtect signatures should now block execution of this specific dropper variant. However, this does not preclude the threat actor from obtaining new developer credentials.
Related Families#
MacSync competes directly with AMOS (Atomic macOS Stealer) in the MaaS market, the dominant macOS stealer family with tens of thousands of detections in 2025. Both families use AppleScript-based credential harvesting and HTTP POST exfiltration to similar endpoint structures.
Recommendations#
Block DNS resolution for
gatemaden[.]spaceandfocusgroovy[.]comat enterprise DNS resolvers and perimeter firewalls.Deploy network detection for the User-Agent string
UserSyncWorker/1.0 (macOS)in HTTP proxy logs and network monitoring systems.Monitor endpoint telemetry for creation of
~/Library/Application Support/UserSyncWorker/or/tmp/osalogging.zipfile paths.Alert on quarantine stripping: Processes invoking
xattrto removecom.apple.quarantinefollowed by execution of the modified file.Verify XProtect is current: Apple has revoked the certificate for TeamIdentifier
GNJLS3UYZ4. Ensure endpoints have updated XProtect definitions.Hunt for API key usage: Look for curl processes with the header value
5190ef1733183a0dc63fb623357f56d6in command-line logging.
Conclusion#
This sample is confirmed as a variant of MacSync Stealer with high confidence based on exact matches across Developer Team ID, C2 infrastructure, payload paths, obfuscation methods, and binary hash. The sample represents the latest evolution in MacSync’s distribution methodology, leveraging code signing and notarization to bypass Gatekeeper without user interaction.
The combination of Gatekeeper bypass, code signature validation, rate limiting, and multi-layer payload obfuscation indicates operators with macOS-specific expertise. The threat actor “mentalpositive” continues to actively develop MacSync Stealer, demonstrating a clear trajectory toward more sophisticated delivery mechanisms.
The use of AppleScript for dynamic command execution and the “osalogging” artifact name strongly suggest credential or keystroke harvesting as the primary objective. While Apple has revoked the certificate used in this campaign, this does not preclude the threat actor from obtaining new developer credentials.
Organisations with macOS endpoints should treat this as an indicator of active targeting by financially motivated threat actors and prioritise deployment of the network and host-based detection recommendations in this report.
Indicators of Compromise#
Network IOCs#
| Type | Indicator | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Domain | gatemaden[.]space | Stage 1 C2 server; payload distribution |
| Domain | focusgroovy[.]com | Stage 2/3 C2 server; command retrieval and exfiltration |
| URL | hxxps://gatemaden[.]space/curl/985683bd660c0c47c6be513a2d1f0a554d52d241714bb17fb18ab0d0f8cc2dc6 | Stage 2 payload download endpoint |
| URL | hxxp://focusgroovy[.]com/dynamic | AppleScript command retrieval endpoint |
| URL | hxxp://focusgroovy[.]com/gate | Data exfiltration endpoint |
| User-Agent | UserSyncWorker/1.0 (macOS) | Stage 1 HTTP requests |
| User-Agent | Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.114 Safari/537.36 | Stage 3 HTTP requests |
| HTTP Header | api-key: 5190ef1733183a0dc63fb623357f56d6 | Stage 3 authentication header |
Host-Based IOCs#
| Type | Path/Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| File Path | ~/Library/Application Support/UserSyncWorker/ | Malware state directory |
| File Path | ~/Library/Logs/UserSyncWorker.log | Execution logging |
| File Path | /tmp/runner | Downloaded payload staging |
| File Path | /tmp/runner.headers | HTTP response header cache |
| File Path | /tmp/runner.code | HTTP status code cache |
| File Path | /tmp/osalogging.zip | Exfiltration archive |
| File Path | ~/gate/etag | ETag cache for conditional requests |
| File Path | ~/last_update | Rate limiting timestamp |
| Code Signature | TeamIdentifier: GNJLS3UYZ4 | Required signature for payload execution (REVOKED) |
| Token | 985683bd660c0c47c6be513a2d1f0a554d52d241714bb17fb18ab0d0f8cc2dc6 | Campaign or victim identifier |
Appendix A: Decoded Stage 3 Payload#
The following is the decoded Stage 3 payload retrieved from the Zsh wrapper script:
| |
Note: The original decoded payload contained the syntax if daemon_function "$@" & then which is invalid Zsh—likely a bug or intentional obfuscation. The functional intent is shown above: background the daemon function and exit immediately.
The daemonisation via file descriptor redirection (exec </dev/null etc.) and the direct pipe from curl to osascript keeps the dynamically retrieved AppleScript entirely in memory.
Appendix B: Detection Rules#
YARA Rules#
| |
Suricata Rules#
| |
Appendix C: Key Binary Functions#
| Function | Address | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| entry | 0x100003fb0 | Main entry point; initialises paths and invokes runInstaller |
| runInstaller | 0x100004a80 | Core logic: rate limiting, download, validation, execution |
| checkInternet | 0x100004780 | Connectivity verification via dispatch semaphore |
| log | 0x1000041d0 | Writes timestamped entries to UserSyncWorker.log |
Appendix D: Extracted Strings#
| |